Threat hunting is a popular buzzword in cybersecurity, but how does it actually work? LogPoint’s Threat Hunting capabilities, including advanced analytics, enrichment, correlations, UEBA, and reporting, will empower you to strengthen your overall security posture with the use of a single interface.
LogPoint also uses threat intelligence feeds to automate some aspects of threat hunting. Threat intelligence feeds are used at the time of ingest, so that when data comes to us, it’s evaluated against all known configured threat intelligence feeds.
Threat intelligence is also used at the time of analysis, allowing analysts to submit any amount of historical data to be evaluated against most recent threat intelligence feeds, to see if they match any new knowledge about attacks. These correlated and evaluated alerts can then be pushed to a third party incident response tool for orchestration and remediation.
LogPoint‘s incident response integrations provide automated workflows for business context enrichment, threat intelligence, and correlation of log data with network data. Based on your organization’s workflow, your security team will be empowered to efficiently gather evidence, build the case and remediate.
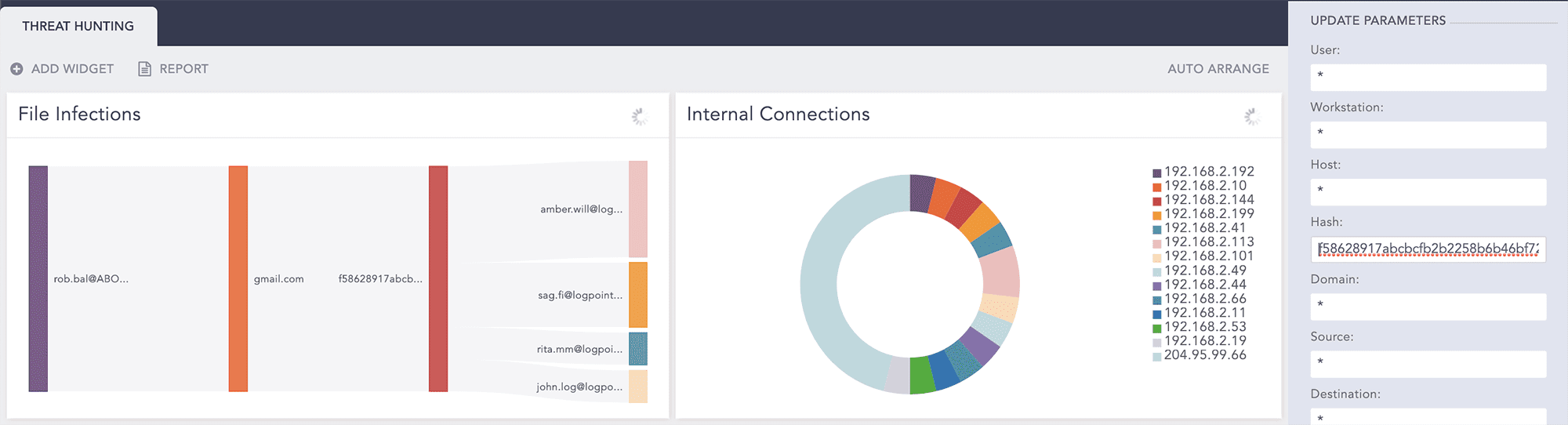
To demonstrate how Threat Hunting actually works, we’ve put together a scenario beginning with file infections dectected using LogPoint. In this example we use our labels to quickly identify infected files.
Step 1: Setting the scene
Example:
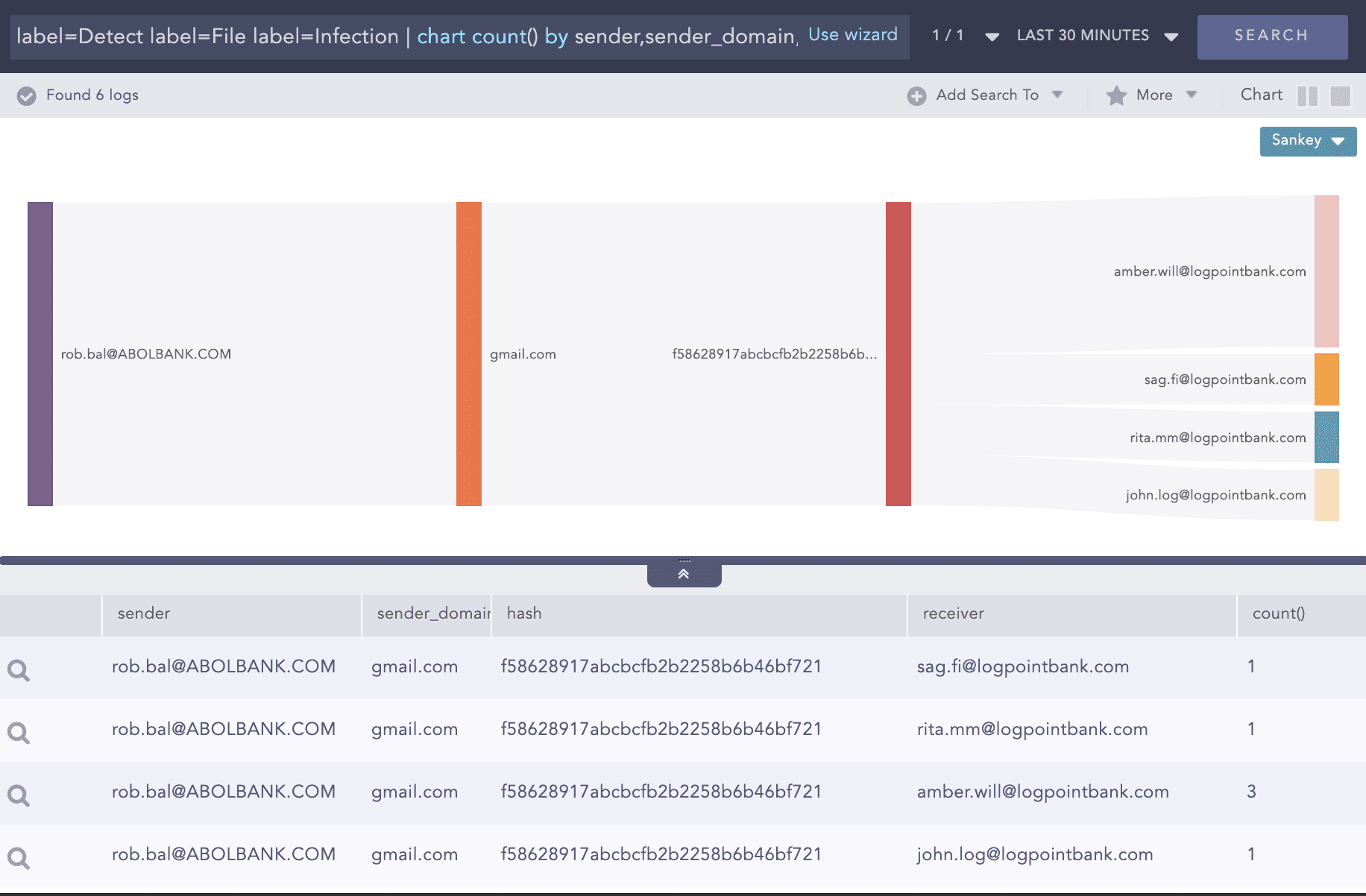
File infections detected
Query:
label=Detect label=File label=Infection | chart count() by sender,sender_domain,hash, receiver
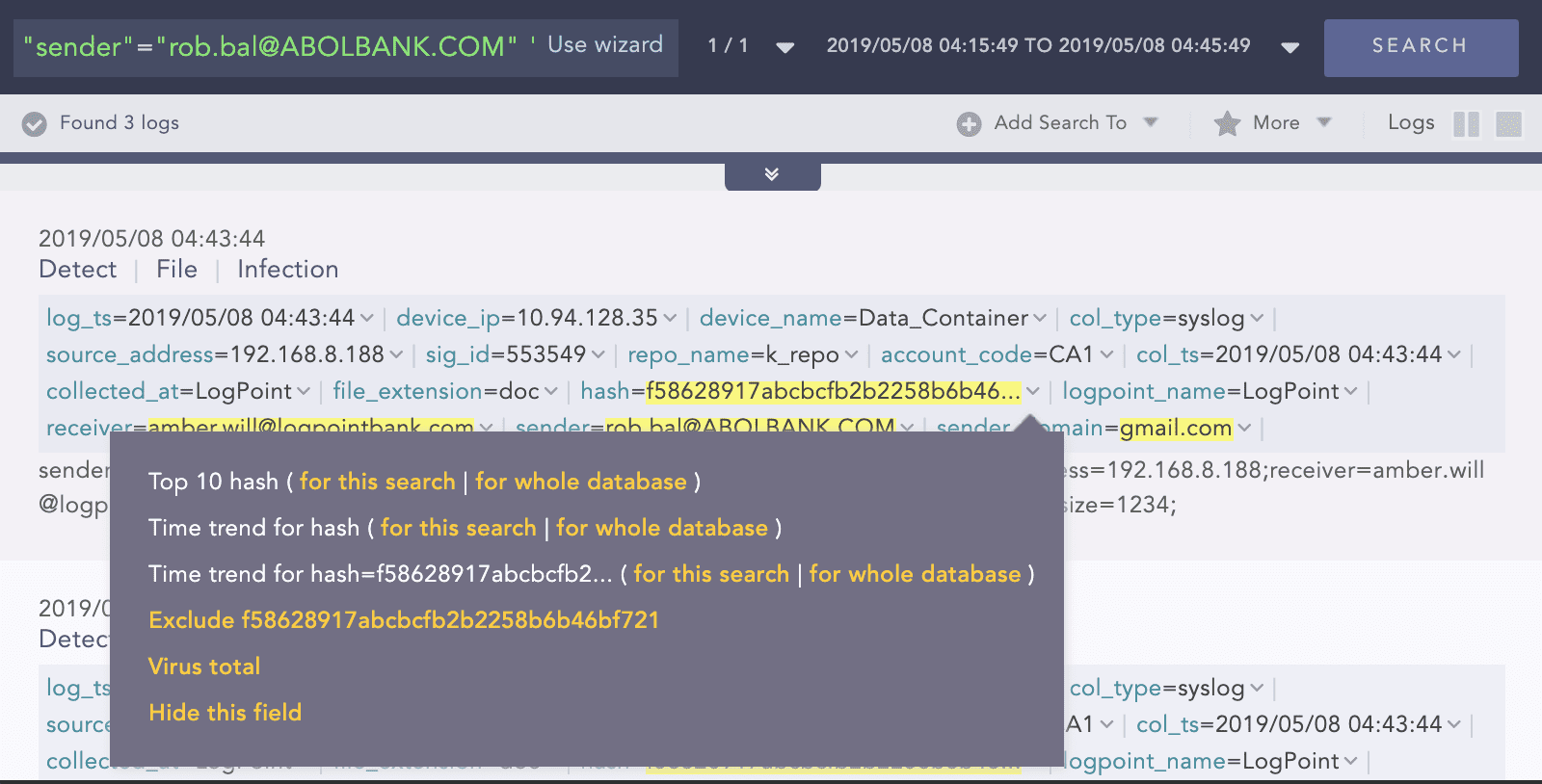
Drill down on the first row and identify the checksum.
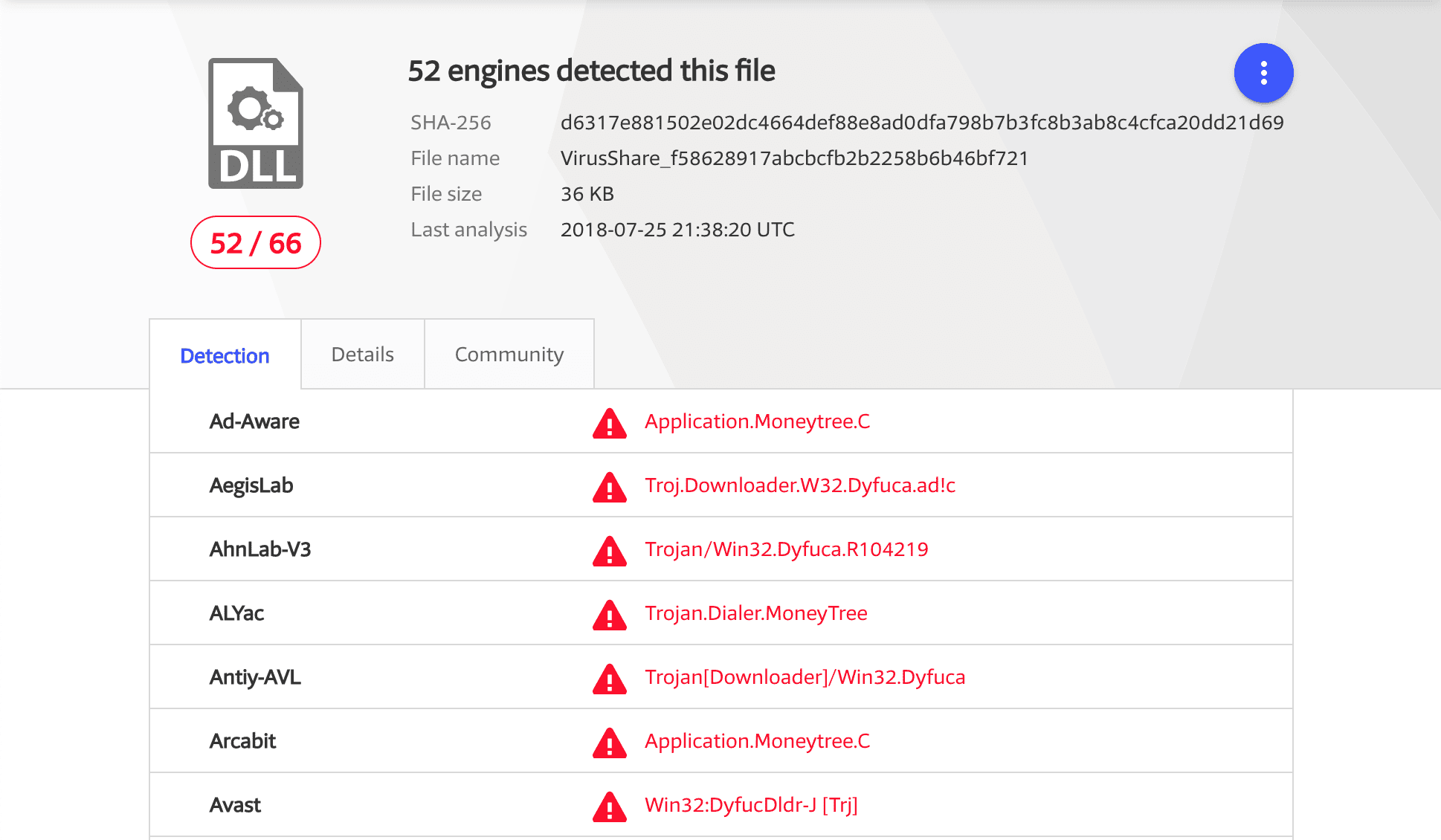
Use to the checksum to drill back to Virus Total
Conclusion: Raise the flag and further investigation required to investigate the impacts of the infection.
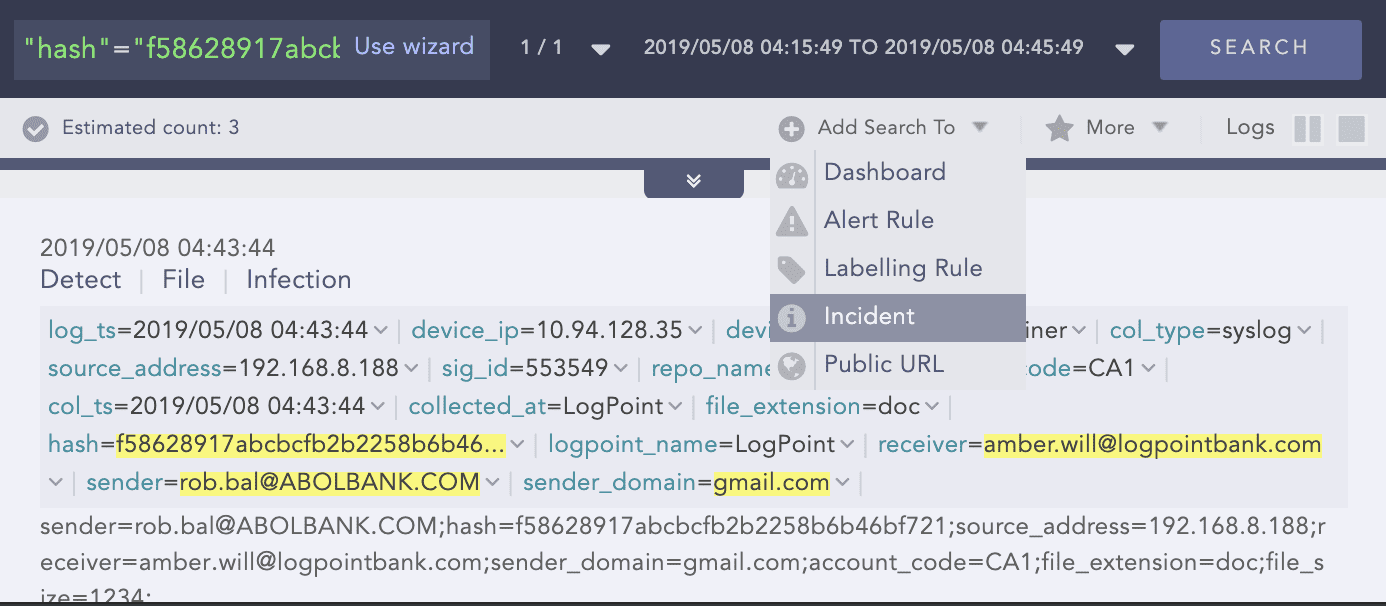
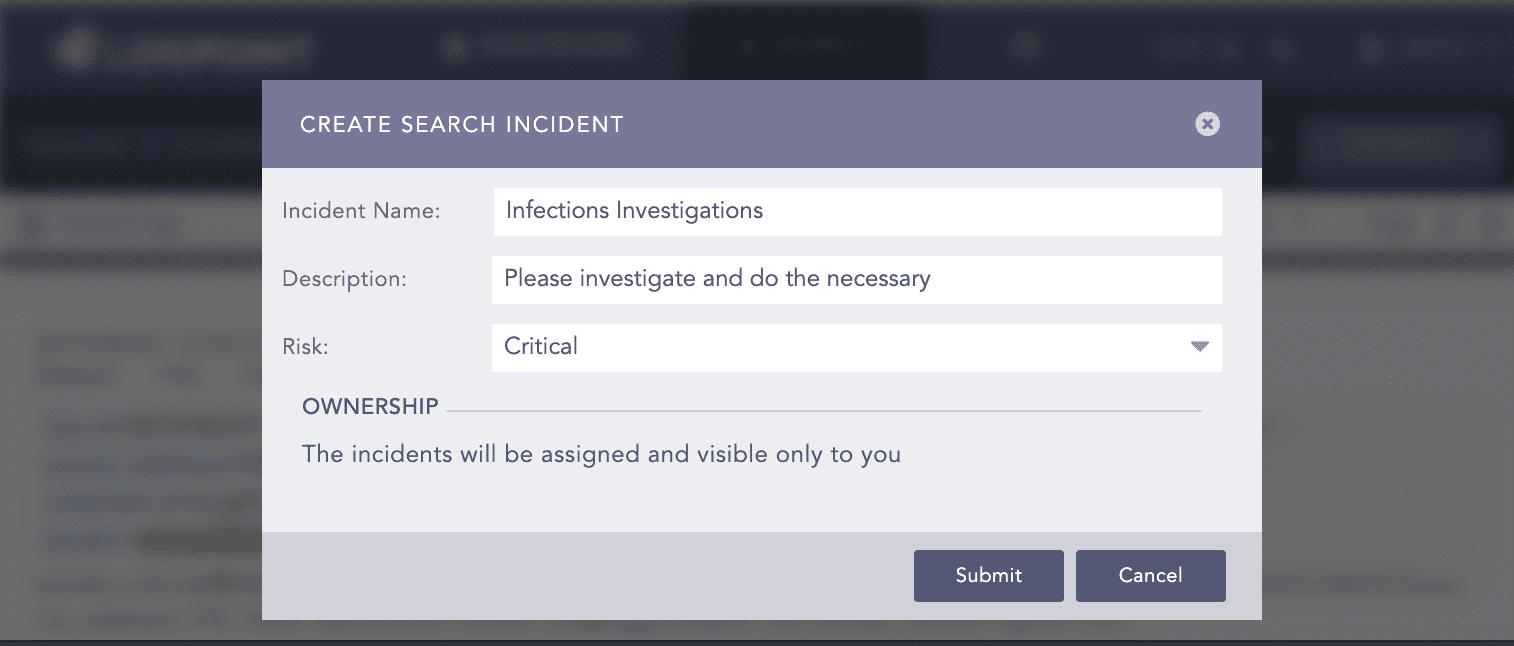
Step 2: Raise flag
Create an incident for follow up.
Step 3: Investigation
Apply the identified hash as the filter.
Pick each user associated with the recipient emails.
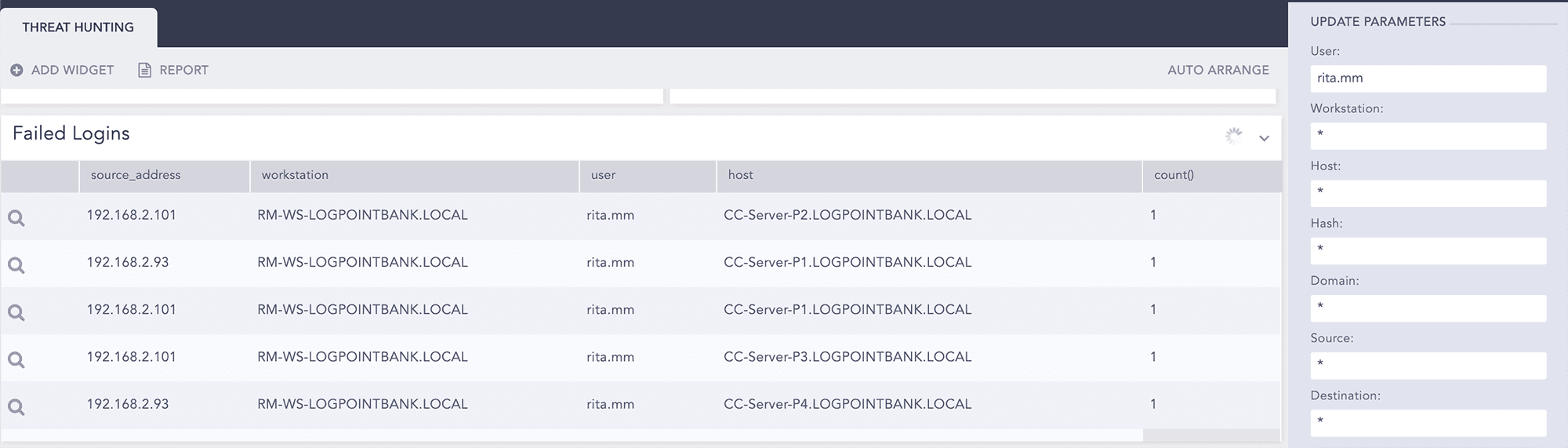
User Rita shows failed login attempts to various servers.
Go to the search page to see the details.
Example:
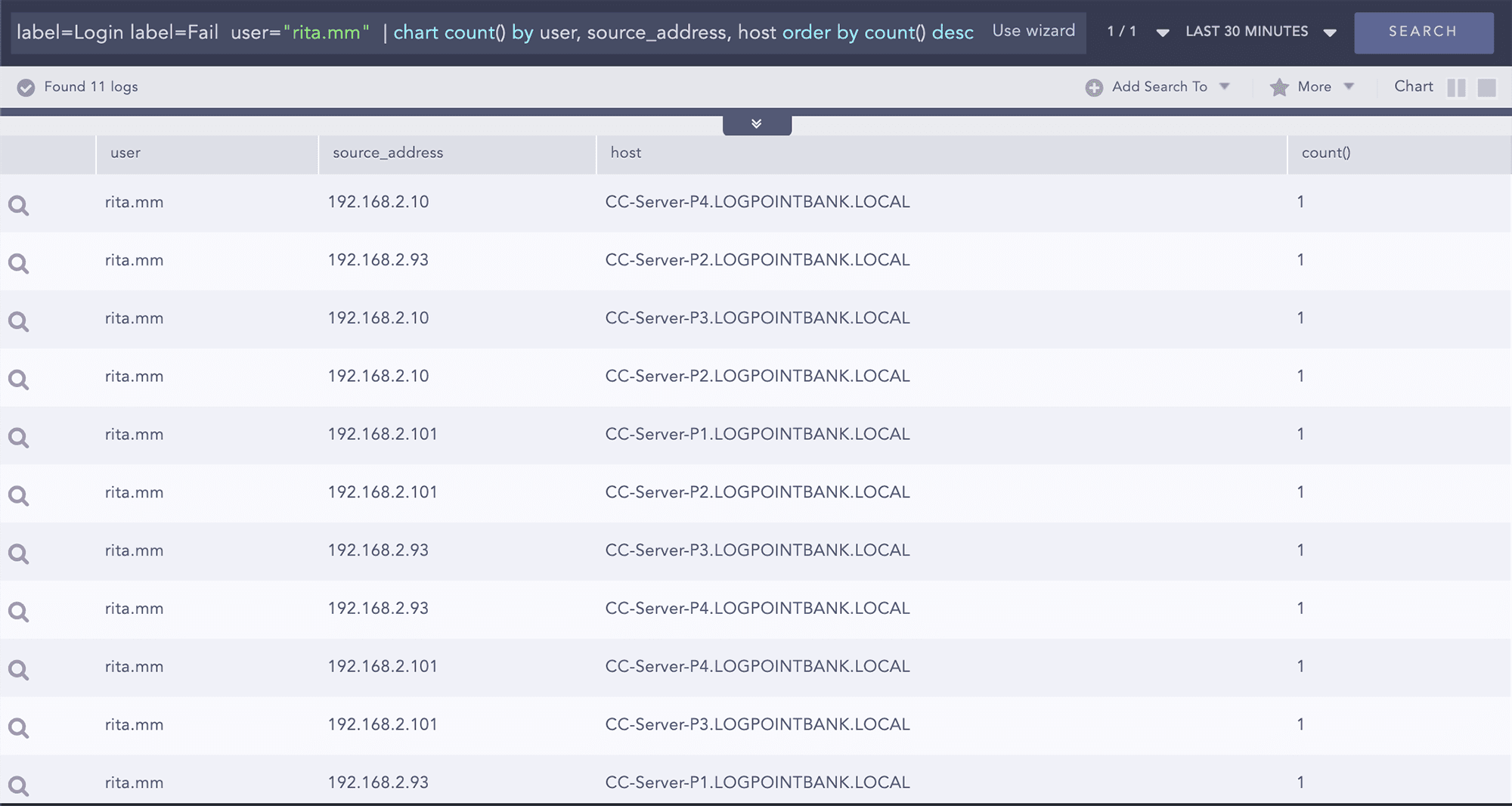
Failed login attempt for specific user
Query:
label=Login label=Fail user="rita.mm" | chart count() by source_address,workstation,user,host order by count() desc
Pick one the source IPs used by user Rita to check if there are other failed attempts or not.
Example:
Failed login attempt for specific source
Query:
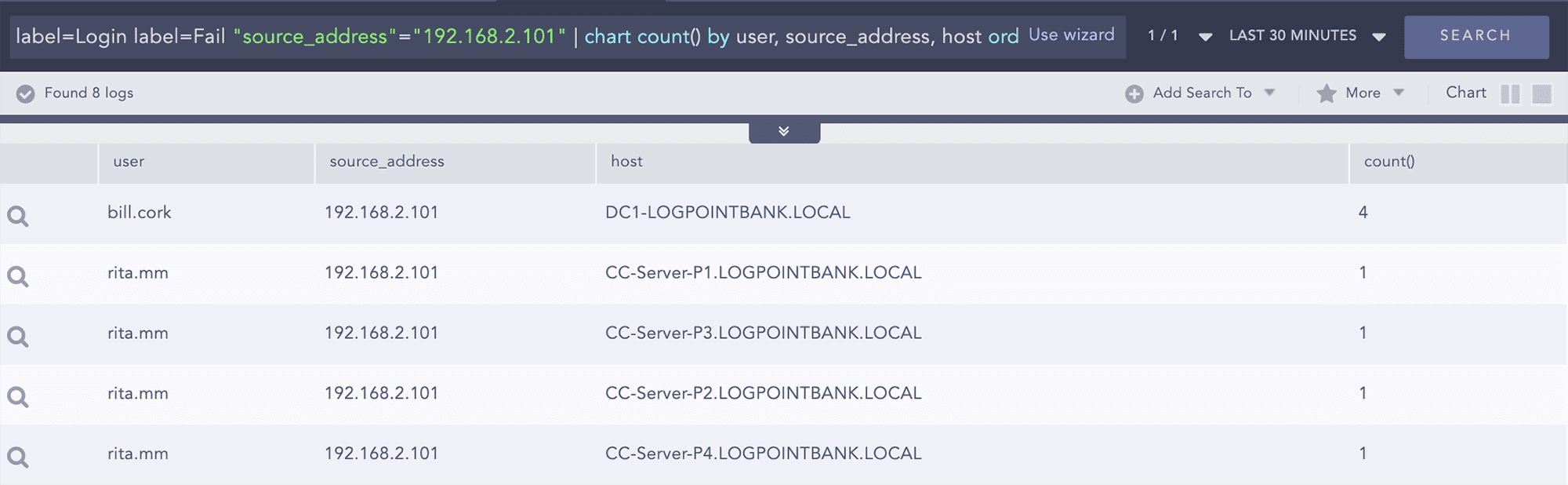
label=Login label=Fail source_address=192.168.2.101 | chart count() by source_address,workstation,user,host
We observe that with source 192.168.2.101 there are 4 failed attempts from the same source.
Drill down on this event.
Example:
Failed login attempt on multiple filters by failure sub status
Query:
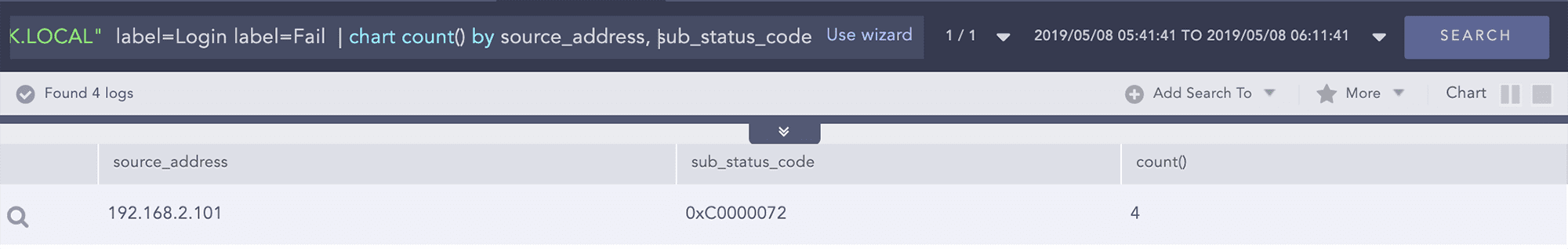
user="bill.cork" source_address=192.168.2.101 host="DC1-LOGPOINTBANK.LOCAL" label=Login label=Fail | chart count() by source_address, sub_status_code
We observe that a disabled account is trying to login to the Domain Controller, the substatus code 0xC0000072 actually relates to login failed on disabled account.
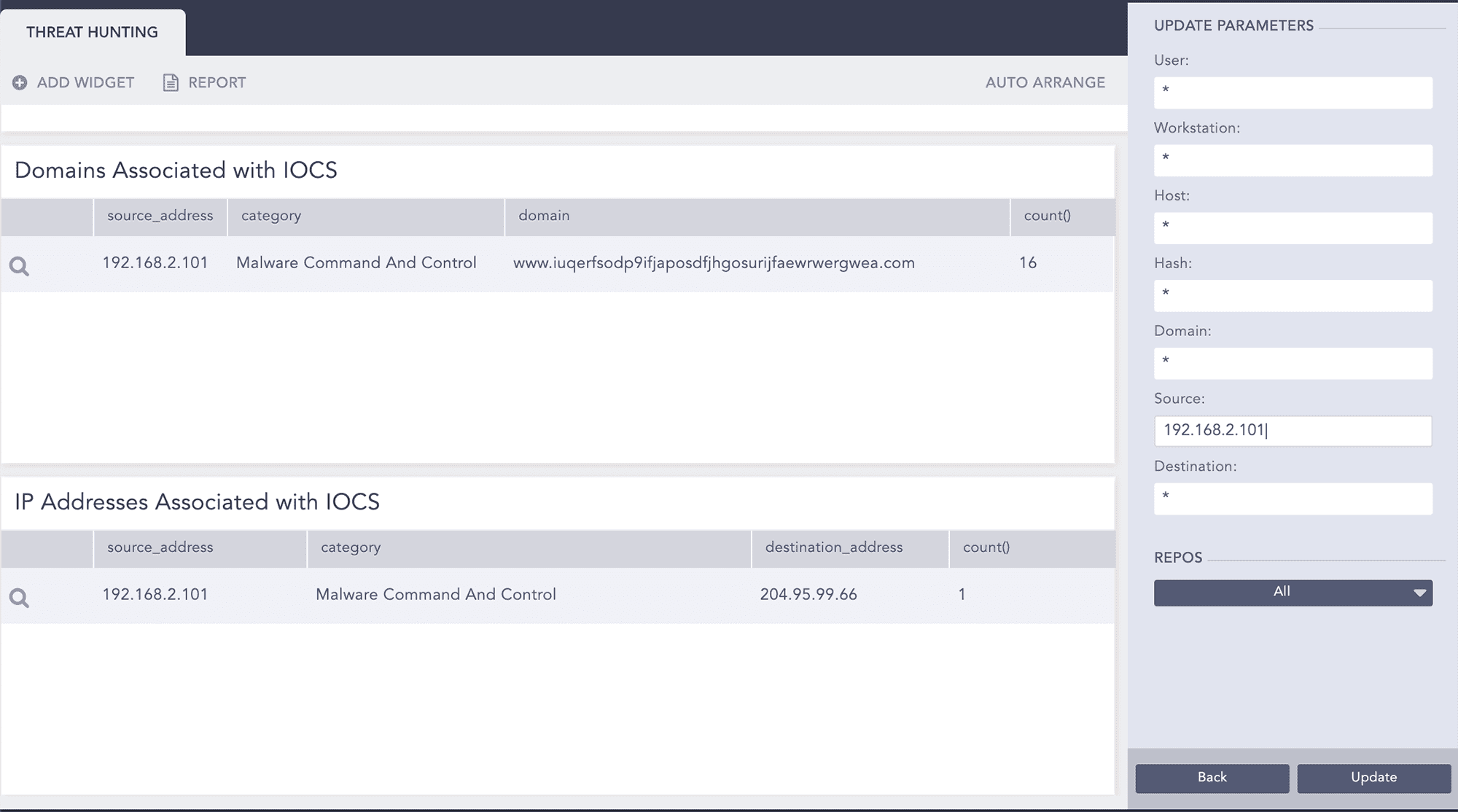
Now we go back to the search template to check for IOCs associated with source 192.168.2.101.
We drill down on category “Malware Command And Control” to check other source addresses associated with it.
Example:
Threat indicators for malware command and control
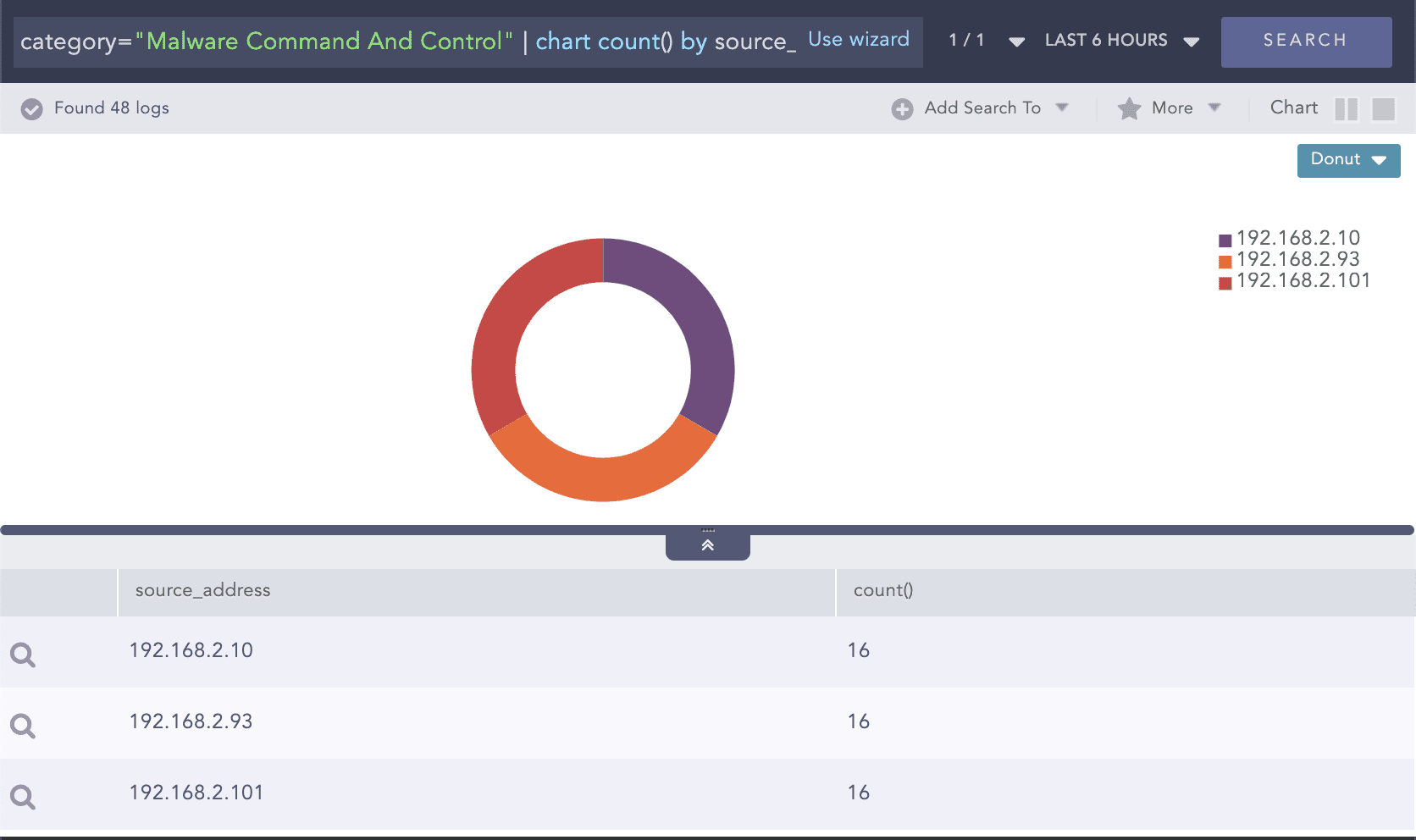
Query:
category="Malware Command And Control" | chart count() by source_address
Step 4: Remediation/Reporting
During the process of threat investigation, we identify that user Rita is compromised and should be disabled. While user Rob should be deleted if not to be enabled in the future.
Carry further investigations on the incident to validate if there were any activities of the identified threat indicators in the past.
Example:
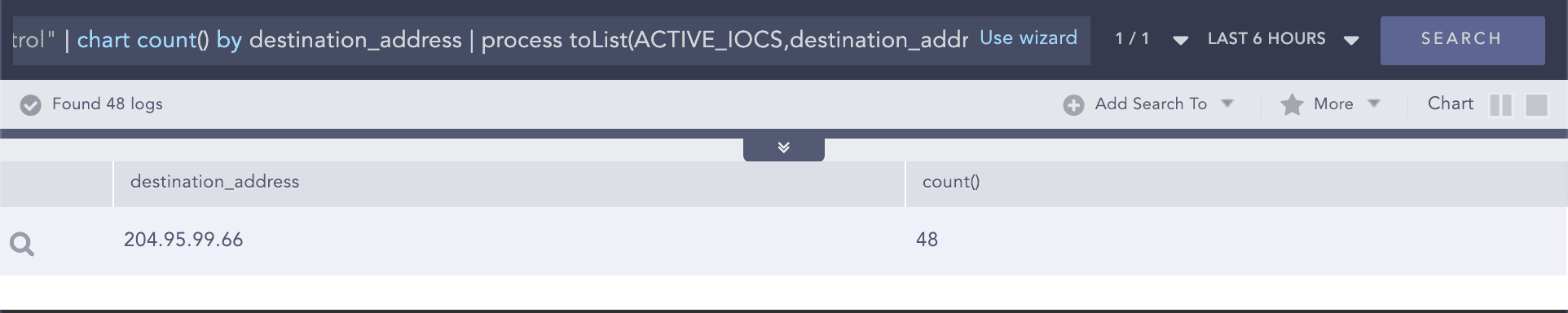
Threat indicators for malware command and control appended to list
Query:
category="Malware Command And Control" | chart count() by destination_address | process toList(ACTIVE_IOCS,destination_address)
Search historical events for any activities associated with the IPs in the ACTIVE_IOCS list.
Example:
Entities observed in list of threat indicators
Query:
source_address IN ACTIVE_IOCS OR destination_address IN ACTIVE_IOCS
The infected systems should be cleaned and the firewall rule should be updated to block the connections to the “Command And Control Servers”.